Radiation Effects
Incident gamma and beta radiation causes extremely little damage in metals, other than will break the chemical bonds and avoid bond recombination of organic compounds and it cause permanent damage. Ionization is the main damage mechanism in organic compounds. Ionization effects are caused through the passage by a material of gamma rays or charged particles like as beta and alpha particles. Even fast neutrons, generating fast protons on collision, lead to ionization as a main damage mechanism. To thermal neutrons the main effect is by (n,gamma) reactions along with hydrogen, within the 2.2 MeV gamma genertaing energetic ionization and electrons. Ionization is particularly important along with materials which have either ionic or covalent bonding.
Ion production inside a chemical compound is expert through the breaking of chemical bonds. This radiation-induced decomposition avoids the use of several compounds in a reactor environment. A Material like as dielectrics, insulators, lubricants, plastics, hydraulic fluids, and rubber are between those which are sensitive to ionization. Plastics along with long-chain-type molecules having varying amounts of cross-linking might have sharp changes in properties because of irradiation. In common, plastics suffer varying degrees of loss in their properties after exposure to high radiation fields. Nylon starts to suffer degradation of its toughness at associatively low doses, other than suffers little loss in strength.
High-density (linear) polyethylene marlex 50 loses both strength and ductility at associatively low doses. In common, rubber will harden upon being irradiated. Therefore, Thiokol or butyl rubber will soften or become liquid along with high radiation doses.
It is significant in which oils and greases be evaluated for their resistance to radiation if they are to be employed in a high-radiation environment. Liquids in which have the aromatic ring-type structures displays an inherent radiation resistance and are well suitable to be used as hydraulics or lubricants.
For a provided gamma flux, the degree of decomposition experiential depends on the categories of chemical bonding present. The chemical bond along with the least resistance to decomposition is the covalent bond. Within a covalent bond, the outer, or valence, electrons are shared through two atoms rather than being firmly attached to someone atom. Organic compounds, and a few inorganic compounds such as water, exhibit this category of bonding. There are considerable differences in the strength of covalent bonds present in compounds of various categories and thus a huge variation in their stability under radiation. The plastics elaborate above could display extremely sharp property changes along with radiation, while polyphenyls are reasonably stable.
One conclusion of ionization is which smaller hydrocarbon chains will be established (lighter hydrocarbons and gases) as well as heavier hydrocarbons through recombination of broken chains into larger ones. This recombination of busted hydrocarbon chains into longer ones is called polymerization.
Polymerization is one of the chemical reactions which takes place in organic compounds in during irradiation and is responsible for modifications in the properties of this material. A few other chemical reactions in organic compounds which could be caused through radiation are halogenation, oxidation, and changes in isomerism. A polymerization mechanism is used in some organizational applications to change the character of plastics after they are in place; for instance, wood is impregnated along with a light plastic and then cross-bonded (polymerized) through irradiating it to make it more sturdy. This change in properties, whether it is a lubricant, electrical insulation, or gaskets, is of concern while selecting materials for use near nuclear reactors. One of the output of the Three Mile Island accident is which utilities have been asked to evaluate whether instrumentation would function in the occasion of radiation exposure being spread since of an accident.
Since neutrons and gamma rays (and other nuclear radiations) produce the similar categories of decomposition in organic compounds, it is general to express the effects as a function of the energy absorbed. One way is to state the energy in terms of a unit known as the rad. A rad represents energy absorption of 100 ergs per gram of material. As an instance of the effects of radiation, Below Figure displays the increase in viscosity along with radiation exposure (in rads) of three organic compounds which may be considered for use as reactor moderators and coolants.
The ordinates represent the viscosity rise associatively to which of the material before irradiation (mostly at 100ºF), so in which they provide a common indication of the extent of decomposition because of radiation exposure. This figure described in which aromatic hydrocarbons (n-butyl benzene) are more resistant to radiation damage than are aliphatic compounds (hexadecane). A most resistant of all is the polyphenyls, of that diphenyl is the easiest example.
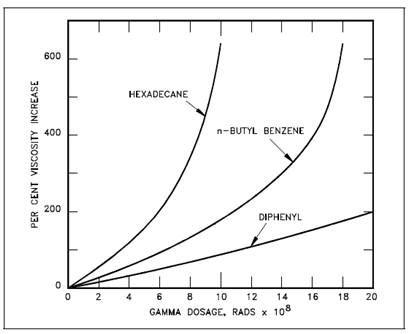
Figure: Effect of Gamma Radiation on Different Types of Hydrocarbon