Proportional Counter:
A proportional counter is a detector that operates within the proportional region.
DESCRIBE the operation of a proportional counter to involve:
a. Radiation detection
b. Quenching
c. Voltage variations
A proportional counter is a detector that operates within the proportional region, as display in Figure. It describes a simplified proportional counter circuit.
To be able to detect a single particle then the number of ions generates must be increased. Because voltage is increased into the proportional region, the major ions obtain enough energy to cause secondary ionizations (gas amplification) and increase the charge collected. Those secondary ionizations may cause further ionization.
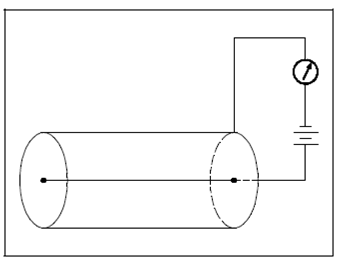
Figure: Proportional Counter
In this region, there is a linear relationship between the number of ion pairs collected and applied voltage. A charge amplification of 104 can be obtained in the proportional region. Through proper functional modifications, arrangements, and biasing, a proportional counter could be used to detect beta, alpha, gamma, or neutron radiation in mixed radiation fields.