Standard addition method:
As you have learnt, this method is especially applicable while the signal is altered through the sample matrix. In that method a known amount of the standard solution of known increasing concentrations of the analyte is added to a number of aliquots of the sample solution. A resulting solution is diluted to the similar last volume and their absorbances are measured. A graph is drawn among the absorbance and the added concentrations of the analyte. It is then extrapolated to the concentration axis to acquire the concentration of sample solution. If the plot is nonlinear then extrapolation is not probable. It is necessary to perform blank correction within such a case. The calibration plot acquired through using standard addition method is display in Figure.
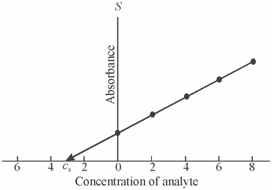
Figure: Calibration plot for standard addition method indicating Cx as the concentration for unknown sample
AAS is a promising analytical method which is extensively employed for quantitative determinations of various elements in huge range of samples. A main drawback of the AAS measurements is in which only a single element could be determined at a time as a separate radiation source is needed for every element. Therefore, nowadays modern instruments are equipped to undertake multielement determinations. Now let us learn about the instrumental aspects of atomic absorption spectrometry.