Opioids
The Opioids are a collection of neurotransmitters that act on opioid receptors, the aim for opiate drugs like the morphine. They are normally co-released with typical transmitters, usually GABA and serotonin, and are generally inhibitory. The Opioid transmission is significant in analgesia pathways in the CNS. The Opioids are encoded by the three precursogenes:
- The enkephalin predecessor encodes met-enkephalin and leu-enkephalin (so called as they vary in merely one amino acid) and is expressed mostly in short interneurons throughout the brain.
- The Pro-opiomelanocortin encodes β-endorphin and is expressed in neurons of the hypo -thalamus that project to the thalamus or brainstem.
- The dynorphin predecessor codes for leu-enkephalin and the dynorphins.
There are three populations of opioid receptors, the properties of that are summarized in table as shown. They are GPCRs that permit direct coupling of G proteins to the ion channels. By opening the K+ channels and closing Ca2+ channels they hyperpolarize the neurons.
The two peptides with high affinity and specificity for µ receptors have newly been specified. The gene or predecessor protein for these endomorphins has not so far been found.A few opioids also interact with NMDA receptors and with σ receptors.
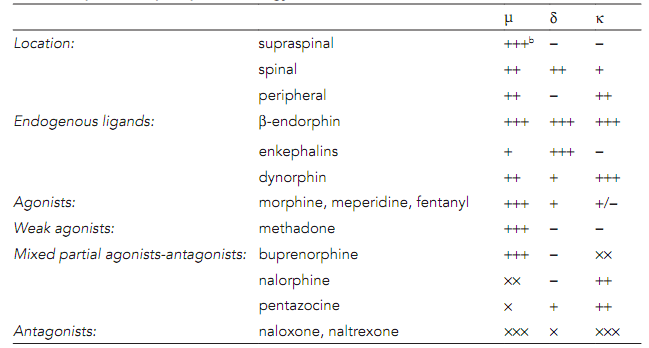
Table: The Opioid receptor pharmacologya