Long-Run Equilibrium of A Monopoly:
Under monopoly, barriers to entry allow profits to remain supernormal in the long run. Therefore, in the long-run a monopoly firm will maximize profit by producing where marginal revenue (MR) is equal to long-run marginal cost (LMC), as long as price (P) is greater or equal to long-run average cost (LAC). It also follows that the monopoly firm is not forced to operate at the minimum point on LAC curve, hence, long run prices will tend to be higher and output lower, under monopoly than under perfect competition, ceteris paribus.
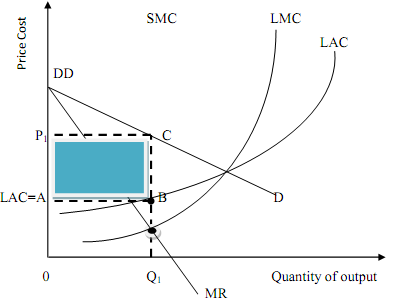
In Figure 8.2, the monopoly firm`s supernormal profit is represented by the shaded rectangle P1 ABC, while the price charged and the profit-maximizing output are given as P2 and Q2 respectively.