Composite gamma ray spectrum:
In order to understand analytical applications derived from a gamma spectrum, let us consider a composite spectrum of 54Mn, 60Co and 137Cs as shown in Figure. In any quantitative analysis using composite gamma ray spectra, area under each photo peak is measured. To do this first part of photo peak lying above the Compton background is selected. This is commonly done by locating the left hand channel (C1) just before the photo peak that appears to rise above the background and the right hand
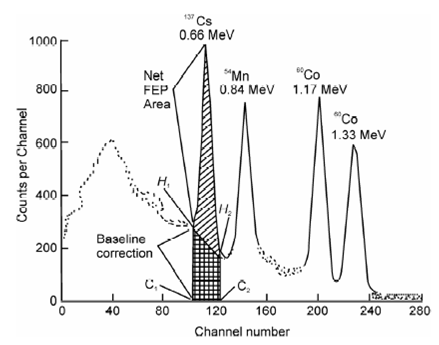
Figure: Composite gamma ray spectrum of 137Cs, 54Mn and 60Co sources recorded on a scintillation gamma ray spectrometer.
channel (C2) at the point where the photo peak disappears into the background. Thus net photo peak area is calculated by using the following formulation.
Net Area (Counts ) =( Total Area/ C1 to C2) - (H1-H2/2)(C2-C1-1)
where total area (C1 to C2) is calculated by adding total counts in each channel from C1 to C2 multiplied by the number of channels. H1 and H2 are the counts in C1 and C2 channels respectively. If the background count distribution around C1 and C2 appear to be horizontal (i.e. H1 and H2 are same) it is often advisable to take average counts in 3 or 5 channels preceding the photo peak and following the photo peak so as to have more representative baseline correction. For routine work, it is advised to record counts at the photo peak position which ensures the selection of photo peak as well as good counting statistics.