Simplified Structure of an Assembled Product:
The bill-of-materials file lists the component parts and subassemblies that make up each product. It is used to compute the requirement for raw materials and components utilized in the end products listed in the master schedule. Figure shows a simplified structure of an assembled product. The product consists of two subassemblies, each of consisting of three parts. (The number of each of item in the next level above in the product structure is indicated in parentheses.)
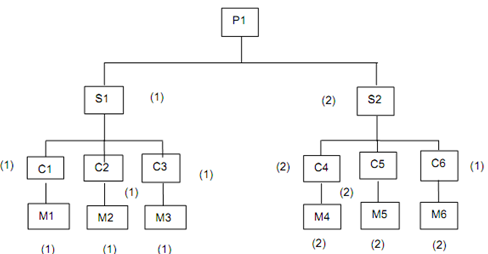
Figure: A Simplified Structure of an Assembled Product
Based on inputs from the master schedule, bill of materials file, and inventory record file, the MRP processor computes how many of each components and raw material shall be needed in future time period by exploding the end product schedule in to successively lower level in the product structure. The capacity for production plan computations should deal with several complicating factors. First, component and subassembly quantities should be adjusted for any inventories on hand or on order. Second, quantities of common use item should be combined during parts explosion to obtain a total requirement for each component and raw material in the schedule. Third, the time phased delivery of end products must be converted in to account its ordering or manufacturing lead times. For each of component of the product, the raw material must be ordered, accounting for its ordering lead time. And assembly lead times should be considered in the scheduling of subassemblies and final products.