Secretory proteins:
Proteins destined to be secreted from the eukaryotic cell are synthesized through ribosomes bound to the RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum). As the protein is synthesized it is translocated across the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane into the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum where it folds into its last conformation. The ER then buds off vesicles which hold the protein to the Golgi apparatus also known as the Golgi complex that is shown in the figure. The Golgi has a cis face (where vesicles enter) and a Tran's face (where vesicles leave). Therefore the RER vesicles fuse with the cis compartment of the Golgi and releasing the protein into the Golgi lumen. The protein then moves by the Golgi complex to the Trans compartment being modified en route through the addition of carbohydrate residues (glycosylation,). At last, vesicles bud from the trans compartment and holds the glycosylated secretory proteins to the plasma membrane where the vesicles fuse, releasing their stuffing to the cell exterior. This extracellular and fusion release of protein is also known as exocytosis.
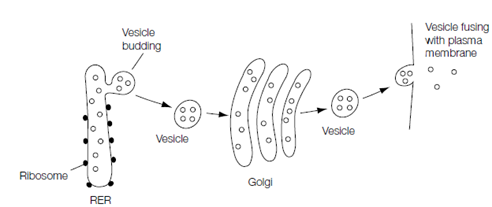
Figure: Synthesis and exocytosis of secretory proteins; see text for details. The ribosomes attached to the RER are shown as filled-in circles whereas the open circles in the lumen of the RER, vesicles and Golgi complex represent secretory protein molecules.