Lysosomal proteins:
Lysosomal lysosomal and enzymes membrane proteins are synthesized on the RER and transported to the cis compartment of the Golgi complex. Now they become mannose and glycosylated 6-phosphate is added to the protein. The mannose 6-phosphate is the signal which targets the lysosomal protein to its right destination. It is identify through mannose 6-phosphate receptor proteins in the trans compartment of the Golgi that bind to the lysosomal protein and package it in transport vesicles which bud from the Golgi apparatus shown in the figure. The transport vesicles then fuse with sorting vesicles, the contents of that are acidic. The low pH causes dissociation of the lysosomal protein from its phosphatase and a receptor erased the phosphate from the mannose 6-phosphate, avoiding it from re-binding to the receptor. The Vesicles bud from the sorting vesicle to return the receptor to the Golgi for re-use receptor recycling and the lysosomal protein is now delivered to the lysosome through vesicle fusion with it that's describe in figure.
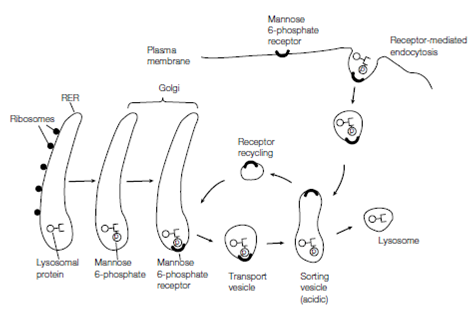
Figure: Synthesis and targeting of lysosomal proteins.
Not all lysosomal proteins take the normal route of protein targeting; some end up being exported through the cell and must be retrieved. This scavenger ways works as go after. The lysosomal glycoprotein binds to mannose 6- phosphate receptors in the plasma membrane and is internalized again through endocytosis. This procedure, known as receptor-mediated endocytosis, creates an endocytic vesicle (or endosome) in which then delivers the lysosomal protein to the lysosome through fusion.