Protein structure determination
Although the presence of the α-helices and the β-pleated sheets in proteins can be predicted from the primary amino acid sequence often, it is not possible to predict the precise 3-dimensional structure of protein from its amino acid sequence,
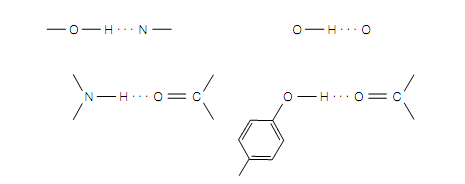
Figure Examples of hydrogen bonds (which are shown as dotted lines).
unless its sequence is similar to that of protein whose 3-dimensional structure is already known to us. Sophisticated physical methods and complex analyses of experimental data are required to determine conformation of protein. The 3-dimensional structure of a protein can be determined to the atomic level by techniques of X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and cryoelectron microscopy.
In X-ray crystallography the 1st requirement are crystals of highly puri?ed protein.In crystal millions of protein molecules are aligned precisely with one another in rigid array characteristic of that specific protein. Beams of X- rays are passed through the crystal as shown in figure given below. The wavelengths of X-rays are 0.1—0.2 nm, short to resolve the atoms in protein crystal. The atoms in the crystal scatter X-rays, producing diffraction pattern of discrete spots on photographic ?lm. The intensities of diffraction maxima (the darkness of the spots on ?lm) are then taken in use mathematically to construct the 3- dimensional image of protein crystal.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is used to determine the 3-dimensional structures of small (up to about 30 kDa) proteins in aqueous solution. It does not require crystallization of the protein. In this method, a concentrated protein solution is placed in magnetic ?eld and effects of different radio frequencies on spin of different atoms in protein measured. The behavior of any particular atom can be in?uenced by neighboring atoms in adjacent residues, with closer residues which causes more perturbation than distant ones. From magnitude of the effect, the distances between residues can be determined and then used to generate the 3-dimensional structure of protein.
Cryoelectron microscopy is used to determine the 3-dimensional structures of proteins, specifically multisubunit proteins, which are difficult to crystallize. In this technique, protein sample is frozen rapidly in liquid helium to preserve its structure.
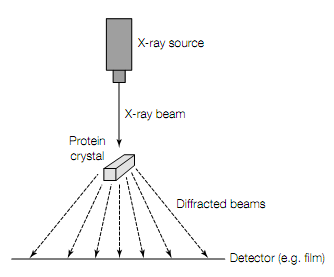
Figure X-ray crystallography. When a narrow beam of X-rays strikes a crystal, part of it passes straight through and rest is scattered (diffracted) in various directions. The strength of the diffracted waves is then recorded on photographic ?lm or with solid-state electronic detector. From diffraction data the 3-dimensional structure of protein can be determined.
in the cryoelectron microscope by using a low dose of electrons to prevent radiation- induced damage to structure. The resulting images can be analyzed by complex computer programs and the 3-dimensional structure of the protein reconstructed.