Primary structure
Introduction: By peptide bonds the linear sequence of amino acids joined together which is termed the primary structure of the protein. Position of covalent disul?de bonds between cysteine residues is included in the primary structure also.
In a protein Primary level of structure is the linear sequence of amino acids as by peptide bonds joined together. By the sequence of nucleotide bases this sequence is determined in the gene encoding the protein .Also included under primary structure is the location of any other covalent bonds. These are chiefly di-sulfide bonds between cysteine residues that can be adjacent in space but not in the linear amino acid sequence. These covalent cross-links between different parts of the same chain or between separate polypeptide chains are composed on cysteine residues by the oxidation of the SH groups that are juxtaposed in space .The resulting di-sulfide is known a cystine residue. Disul?de bonds are frequently present in extracellular proteins, but found rarely in intracellular proteins. Some proteins, like collagen, contain covalent cross-links composed between the side-chains of Lys residues .
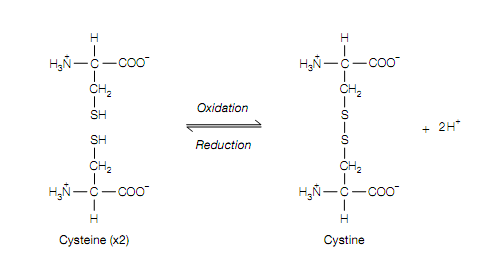
Figure:Creation of a disul?de bond between 2 cysteine residues, producing a cystine residue.