Gel filtration chromatography
In gel filtration chromatography (molecular sieve chromatography or size exclusion chromatography), molecules are divided on the basis of their shapes and sizes. The protein sample in a small volume is applied to the top of a column of porous beads (diameter 0.1 mm) which are made of an insoluble but highly hydrated polymer like as polyacrylamide Bio-Gel or the carbohydrates dextran (Sephadex) or agarose (Sepharose) in Figure. Larger or more elongated molecules cannot whereas Small molecules can enter the pores in the beads. The smaller molecules thus have a larger volume of liquid accessible to them; both the liquid surrounding the porous beads and which inside the beads. In compare, the larger molecules have only the liquid surrounding the beads accessible to them, and therefore move by the column faster, emerging out of the bottom (eluting) first. The smaller molecules move more slowly by the column and elute later. Beads of different pore sizes are available allowing proteins of various sizes to be efficiently separated. The Gel ?ltration chromatography is often used to de-salt a protein sample for instance to erase the ammonium sulfate after ammonium sulfate precipitation, because the salt enters the porous beads and is eluted late, while the protein does not enter the beads and is eluted before. The Gel filtration chromatography can also be used to estimate the molecular mass of a protein.
Figure: Separation of molecules on the basis of size by dialysis. (a) Starting point, (b) at equilibrium.
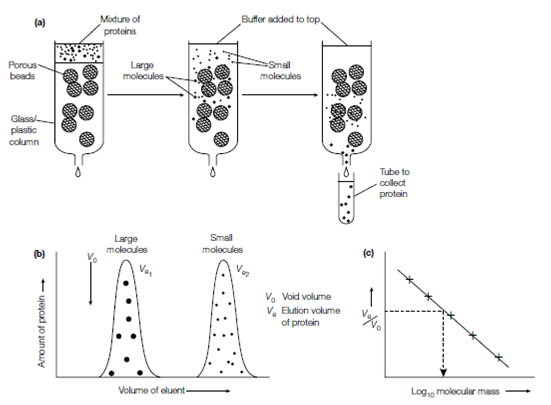
Figure: Gel ?ltration chromatography. (a) Schematic illustration of gel ?ltration chromatography; (b) elution diagram indicating the separation; (c) a plot of relative elution volume versus the logarithm of molecular mass for known proteins, indicating how the molecular mass of an unknown can be read off when its relative elution volume is known.
There is a linear connection among the relative elution volume of a protein (Ve or Vo where Ve is the elution volume of a provided protein and Vo is the void volume of the column, which is the volume of the solvent space surrounding the beads) and the logarithm of its molecular mass. Therefore a standard curve of Ve or Vo against log10 molecular mass can be determined of known mass for the column using proteins . The elution volume of any sample protein then permits its molecular mass to be estimated through reference to its position on the standard curve.