Affinity chromatography
Affinity chromatography developed the high affinity, specific, noncovalent binding of a protein to another molecule the ligand. At first the ligand is covalently attached to porous matrix and an inert like as Sepharose. The protein combination is then passed down a column containing the immobilized ligand. The protein of interest will connect to the ligand, while all other proteins pass straight by the column. After extensive washing of the column with buffer to erase nonspeci?cally bound proteins the bound protein is free from the immobilized ligand either through adding soluble ligand that competes with the immobilized ligand for the protein or through shifting the properties of the buffer like changing the salt concentration or pH. If soluble ligand is used to elute the protein from the column extensive dialysis frequent then has to be used to erase the small ligand from the larger protein. Because this method exploits the frequently unique, speci?c, binding properties of the protein it is quite possible to divide the protein from a mixture of hundreds of other proteins in a single chromatographic step. Generally employed combinations of immobilized ligand and protein to be puri?ed used in affinity chromatographic systems involve an inhibitor to purify an enzyme, an antibody to purify its antigen, a hormone for example insulin to purify its receptor, and a lectin for example concanavalin A to purify a glycoprotein. Advances in recombinant DNA technology mean which proteins can be engineered with specific sequences of amino acids at the C- terminal end a so-called tag. A recombinant tagged protein can then be expressed in a suitable cell system and the af?nity of the tag for an immobilized antibody or other molecule exploited to purify the protein.
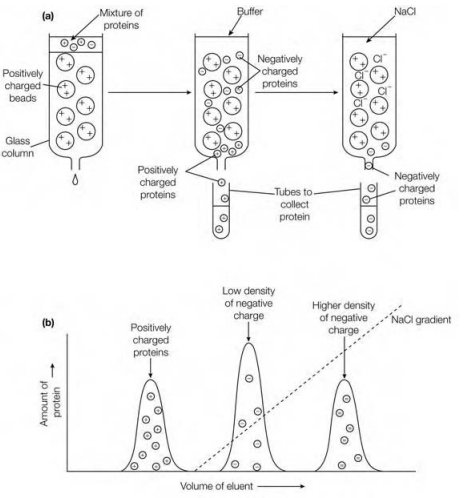
Figure: Affinity chromatography. (a) Schematic diagram of affinity chromatography; (b) elution diagram indicating that nonspecific proteins that do not bind to the immobilized ligand pass straight through the column, while the speci?c protein binds to the immobilized ligand and is eluted from the column only on addition of soluble ligand.