Definition of Derivative Control:
A device which generates a derivative signal is called a differentiator. Figure displays the input versus output relationship of a differentiator.
The differentiator gives an output which is directly associated to the rate of change of the input and a constant which specifies the function of differentiation. A derivative constant is expressed in units of seconds and describes the differential controller output.
The differentiator acts to transform a changing signal to a constant magnitude signal as displays in Figure. As long as the input rate of change is constant then a magnitude of the output is constant. The new input rate of change would provide a new output magnitude.
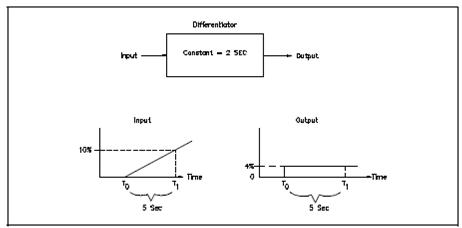
Figure: Derivative Output for a Constant Rate of Change Input
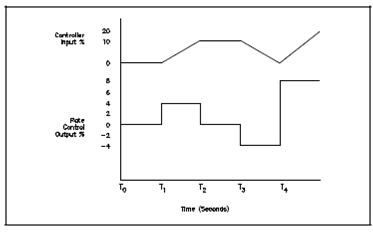
Figure: Rate Control Output