Steam Tables
The Steam tables contains two sets of tables of the energy transfer properties of steam and water: The saturated steam tables and superheated steam tables. Both sets of tables are tabulations of temperature (T), pressure (P), specific volume (ν), specific enthalpy (h), & specific entropy (s). The notation below is employed in steam tables. Some tables employ v for ν (i.e., specific volume) since there is little prospect of puzzling it with velocity.
T = temperature (°F)
P = pressure (psi)
ν = specific volume (ft3/lbm)
νf = specific volume of saturated liquid (ft3/lbm)
νg = specific volume of saturated vapor (ft3/lbm)
νfg = specific volume change of vaporization (ft3/lbm)
h = specific enthalpy (Btu/lbm)
hf = specific enthalpy of saturated liquid (Btu/lbm)
hg = specific enthalpy of saturated vapor (Btu/lbm)
hfg = specific enthalpy change of vaporization (Btu/lbm)
s = specific entropy (Btu/lbm-°R)
sf = specific entropy of saturated liquid (Btu/lbm-°R)
sg = specific entropy of saturated vapor (Btu/lbm-°R)
sfg = specific entropy change of vaporization (Btu/lbm-°R)
Sh = number of degrees of superheat (°F)
The saturated steam tables offer the energy transfer properties of saturated water and saturated steam for temperatures ranges from 32 to 705.47°F (i.e., the critical temperature) and for the equivalent pressure ranges from 0.08849 to 3208.2 psi. Generally, the saturated steam tables are separated into two portions: temperature tables that list the properties according to the saturation temperature (Tsat); and pressure tables, that list them according to the saturation pressure (Psat). The values of entropy and enthalpy given in such tables are measured associative to the properties of saturated liquid at 32°F. Therefore, the enthalpy (hf) of saturated liquid and the entropy (sf) of saturated liquid have values of around zero at 32°F.
Most of the practical applications employing the saturated steam tables include steam-water mixtures. The key property of such mix is steam quality (x), stated as the mass of steam present per unit mass of steam-water mixture, or steam moisture content (y), stated as the mass of water present per unit mass of steam-water mixture. The relationships below exist among the quality of a liquid-vapor mixture and the enthalpies, specific volumes, or entropies of both phases and of the mixture itself. Such relationships are used by the saturated steam tables.
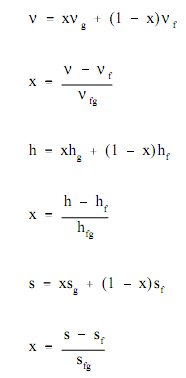
In order to resolve the problems in Thermodynamics, information regarding the "state" of the substance studied should be acquired. Generally, two properties (for illustration, v, p, T, h, s) of the substance should be known in order to examine the other desired properties. Such other properties are generally acquired utilizing either the Mollier diagram (when the substance is steam) or the saturated and superheated steam tables.