Keto-enol tautomerism
Ketones that have hydrogen atoms on their α-carbon (the carbon next to the carbonyl group) are in quick equilibrium along with an isomeric structure termed as an enol in which the α-hydrogen ends up on the oxygen in place of the carbon. The two isomeric forms are called tautomers and the process of equilibration is termed as tautomerism.
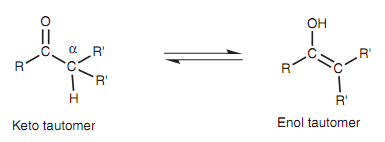
Figure: Keto-enol tautomerism
Generally, the equilibrium very much favors the keto tautomer and the enol tautomer may only be present in extremely small quantities. The tautomerism mechanism is catalyzed through acid or base. While catalyzed by acid, the carbonyl group works as a nucleophile with the oxygen by using a lone pair of electrons to create a bond to a proton.
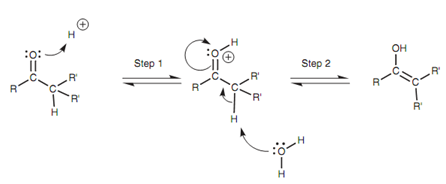
Figure: Acid-catalyzed mechanism for keto-enol tautomerism.