Gibbs-Dalton Laws:
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
Let a homogeneous mixture of non-reacting ideal gases 1, 2, etc., at temperature T, pressure p & volume V as illustrated in Fig 1.
Assume the number of moles of individual gases be n1, n2,...etc. ,and their respective masses is m1, m2, ...etc. Later we have for overall number of moles n and net mass m
n = n1+ n2 + .....= ∑ ni ...6.1
m = m1 + m2 +......=∑ mi ...6.2
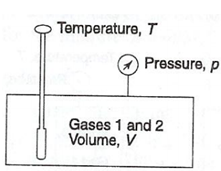
Gas Mixture
Here i refer the number of each of gas.
In the Dalton's model, each of the gas is conceived of as existing separately at the temperature T and net volume V of the mixture as illustrated in Figure 2.
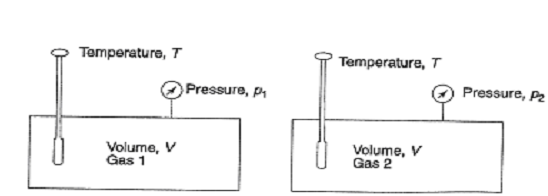
Illustrating Dalton's Model
If one were to compute the pressures exerted through individual gases, they would be found to be p1,p2, ....etc., like., less than the net pressure p of the mixture. These are referred as partial pressures. Letting mixture and each of component gas existing separately at T & V, we have for a binary gas mixture:

Therefore, for a mixture of ideal gases, the net pressure p is equivalent to the sum of the partial pressures. It is known as the Dalton's law of partial pressures.
p = p1 + p2 or p = ∑i pi