Degree of Saturation:
Let the water vapour in the super heated thermodynamic state 1 in unsaturated moist air demonstrating the control volume V. the water vapour present at the dry bulb temperature T of the mixture & partial pressure pv as illustrated in the Figure 4 (b).
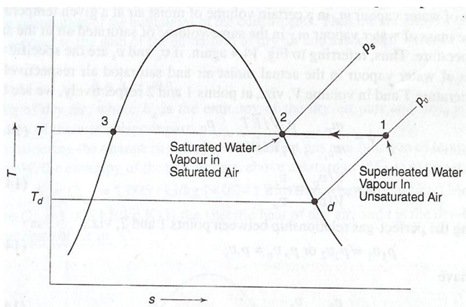
(b) : An Imaginary Isothermal Process Showing the Change of State of Water Vapour
Now refer that more water vapour is added up in this control volume V at temperature T itself. The partial pressure pv shall go on rising with the addition of water vapour till it attain a value ps equivalent to state 2 in given figure after that it may not enhance further as ps is the saturation pressure or utmost possible of water at temperature T. Now the thermodynamic state of water vapour is saturated at pt 2. The air having moisture in such a state is known as saturated air. In this state the air is holding up the utmost amount of water vapour (the specific humidity being ωs, related to the partial pressure ps ) at temperature T of the mixture. The maximum probable specific humidity, ωs at temperature T is therefore
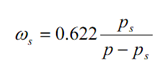 ...6.14
...6.14
The ratio of the real specific humidity ω to the specific humidity ωs of saturated air at temperature T is known as the degree of saturation mentioned by the symbol μ. Therefore
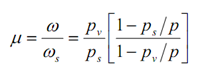 ...6.15
...6.15
Therefore the degree of saturation is a measure of the capacity of air to soak up moisture.