Epoxides:
Epoxides or oxiranes are three-membered cyclic ethers and different from other cyclic and acyclic ethers in that they are reactive to several reagents. The cause for this reactivity is the strained three-membered ring. Reactions along with nucleophiles can effect in ring opening and relief of strain. Nucleophiles will attack either of the electrophilic carbons available in an epoxide through an SN2 reaction.
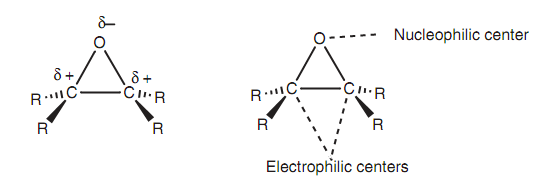
Figure: Properties of an epoxide.
Thioethers
Thioethers or sul?des are the sulfur equivalents of ethers (ROR). Because the sulfur atoms are polarizable, they can stabilize a negative charge on an adjacent carbon atom. The meaning of this is that hydrogens on this carbon are more acidic than those on comparable ethers.