Sieve Analysis, Fineness Modulus and Grading
Sieve Analysis:
Sieve analysis is a procedure for finding the proportion of different standard size fraction of aggregates present in a sample. For this, the aggregate sample is sieved through a set of standard sieves taken in order. The sieves are arranged in descending order from top to bottom with sieve of maximum size at top. As per IS 2386 (Part-I) : 1963 the sieve sets are taken in the following order : 80 mm, 40 mm, 20 mm, 10 mm, 4.75 mm, 2.36 mm, 1.18 mm, 600 μm, 300 μm, and 150 μm. (You may note that size of any sieve is about half of the previous sieve.)
For performing the sieve analysis and appropriate weight of aggregate sample is taken as per the IS 2386 (Part I): 1963 and are given in Table. The weight of sample to be taken depends upon the maximum size of aggregate present substantially in the sample.
Table: Minimum Weight of Aggregate Sample to be taken for Sieve Analysis
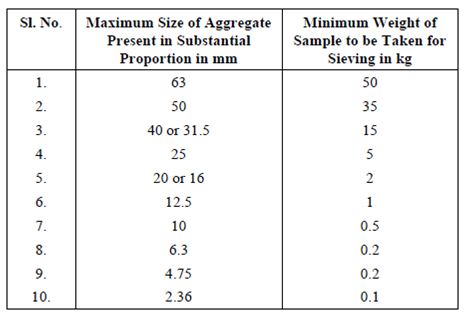
Table gives a sample calculation of sieve analysis to determine various related parameters. After sieving the aggregate sample (1000 gm) through the set of sieves in standard manner, the material retained on every sieve is measured through weight and tabulated in Column 2 of the table. The weight retained on every sieve represents the size-range of particles. For instance, weight retained on 2.36 mm sieve (i.e. 120 gm) denotes in which this particular fraction of aggregate is having the particles of size > 2.36 mm and < 4.75 mm.