Flakiness And Elongation Index
Flakiness Index
Aggregate is termed as flaky when its least dimension (i.e. thickness) is reasonably small relative to its other two dimensions (i.e. width and/or length). The amount of flakiness is denoted by flakiness index.
Flakiness index is given as the percentage by weight of particles in the sample of aggregate whose least dimension is less than 3/5 of the mean dimension (i.e. mean sieve size fraction to which the particle belongs). For example, if we have aggregate sample of 20 mm mean size then any particle of this sample of thickness less than 12 mm (i.e. (3/5) × 20) will be designated as flaky aggregate.
It is measured with the help of standard metal thickness gauge as shown in Figure and as described in IS : 2386 (Part I) - 1963. The thickness gauge has apertures of various sizes. A sample of aggregate is taken and sieved through a set of sieves ranging from 63 mm to 6.3 mm and particles of each fraction are collected divided. The aggregate sample should be taken in sufficient quantity so that each fraction sample should have at least 200 particles. Now, particles of each fraction are allowed to pass through the corresponding aperture individually. The flakiness index is calculated as below:
Flakiness Index = Weight of particles passing through thickness gauge/ Total weight of the sample × 100
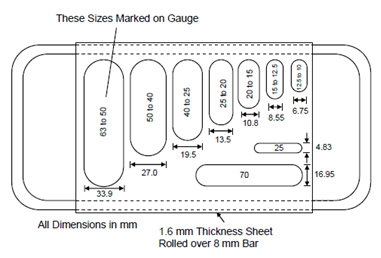
Figure: Thickness Gauge (For Determining Flakiness Index)