Bacterial cell walls
Most prokaryotes are surrounded by a rigid 3-25 nm thick cell wall to protect the cell from mechanical injury and osmotic pressure. Cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan, a complicated of proteins and oligosaccharides. The oligosaccharide component consists of linear chains of alternating N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) linked β(1-4)and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). Attached using an amide bond to the lactic acid group on NAM is a D-amino acid-containing tetrapeptide. Neighbouring parallel peptidoglycan chains are cova- lently cross-linked through the tetrapeptide side-chains by other short peptides. In the peptidoglycan cell the extensive cross-linking wall gives it its rigidityand strength. In the peptidoglycan renders, the presence of D-amino acids he cell wall resistant to the action of proteases which act on the more commonly
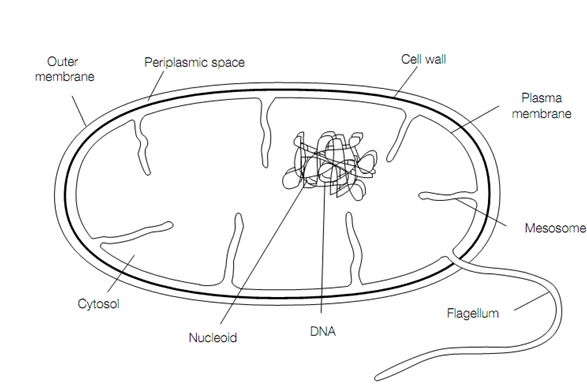
Prokaryote cell structure
occurring L-amino acids but for the action of certain antibiotics such as penicillin provides a unique target . By inhibiting the enzyme Penicillin acts that forms the covalent cross-links in the peptidoglycan, thereby weakening the cell wall. By the enzyme lysozyme The β(1-4) glycosidic linkage between NAM and GlcNAc is susceptible to hydrolysis which is present in tears, mucus and other body secretions.
Bacteria may be classified as either Gram-positive or Gram-negative based on whether or not they take up the Gram stain. Gram-positive bacteria (For example :Bacillus polymyxa) have a thick (25 nm) cell wall surrounding their plasma membrane, whereas Gram-negative bacteria (For example Escherichia coli) have a thinner (3 nm) cell wall and a second outer membrane .on the contrary this outer membrane is very permeable to the passage of relatively large molecules (molecular weight > 1000 Da) with the plasma membrane, due to porin proteins which form pores in the lipid bilayer. Wall is the periplasm between the outer membrane and the cell, a space taken by proteins secreted from the cell.