Steel Making
Steel was first produced in China and Japan in about 600-800 AD. The process is essentially one of refining the pig iron obtained from the blast furnace. The refining of pig iron consists of reduction of the percentage of manganese, carbon, silicon & other elements, and control of its composition by the addition of various elements. The molten metal through the blast furnace is transported into one of three kinds of furnace. The steel making furnaces are electric, open hearth, or basic oxygen. The name open hearth derives from the shallow heart shape that is open directly to the flames that melt the metal. Developed in the year of 1860s, the open-hearth furnace is being replaced by electric furnace and by the basic-oxygen process. These newer methods are more capable and generate better quality steels.
The electric furnace was first introduced in the year of 1906. The source of heat is a continuous electric arc formed between the electrodes & the charged metal. Temperature as high as 1925oC are generated in this kind of furnace. There are generally three graphites electrodes in direct arc electric furnace, and they might be as large as 750 mm in diameter & 1.5 to 2.5 m in length. Their height in the furnace might be adjusted depending on the amount of metal present and water of the electrodes.
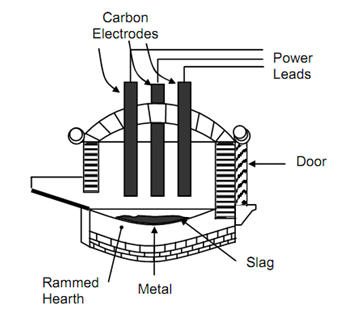
Figure : Direct Arc Electric Furnace
Steel scrap and a small amount of carbon and limestone are dropped into electric furnace throughout the open roof. Electric furnaces might also use 100 percent scrap as its charge. Then the roof is closed and the electrodes are lowered. Power is turned on, and in a period of around two hours the metal melts. The current is stop, the electrodes are increased, the furnace is titled, and the molten metal is poured into a ladle, which is a receptacle used for transferring and pouring molten metal. Electric-furnace competences range through 60 to 90 tons of steel per day. The quality of steel generated is better than that of open-hearth or basic-oxygen process.
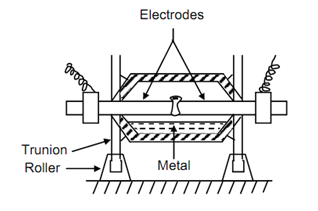
Figure: Indirect Arc Electric Furnace
The induction type electric furnace is utilized for smaller quantities. The metal is placed in crucible, built of refractory material and surrounded with a copper coil through which alternating current is passed. The induced current within charge melts the metal. These furnaces are also utilized for re-melting metal for casting.
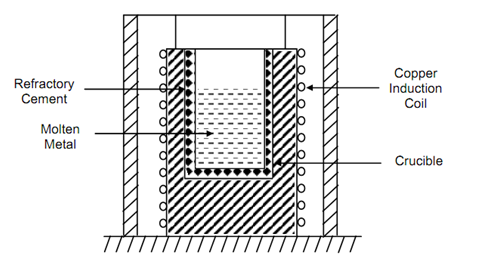
Figure: Induction Type Electric Furnace
The basic-oxygen furnace (BOF) is the newest & fastest steel building procedure. Normally, 200 tons of molten pig iron & 90 tons of scrap are charged into a refractory lined barrel shaped vessel known as converter. Then pure oxygen is blown into the furnace for around 20 minutes under a pressure of approx 1250 kPa, through a water-cooled lance, as illustrated in Figure 5(b). Fluxing agents, such like burnt lime are added through a chute.
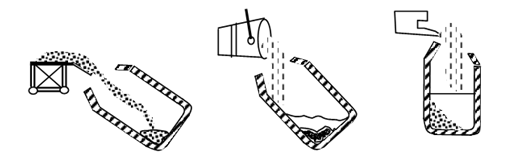
(a) Charging Scrap into Furnace Charging Molten Addition of Iron Burnt Lime
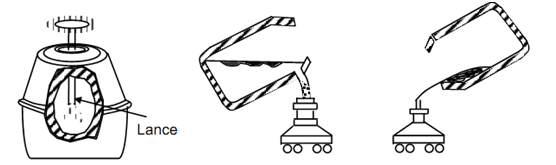
b) Blowing with Oxygen (c) Tapping the Furnace (d) Pouring the Slag
Figure: Basic Oxygen Process of Steel Making Illustrated through Various Operations
The vigorous agitation by the oxygen refines the molten metal through an oxidation procedure in which iron oxide is first generated. The oxide reacts along the carbon in the molten metal, generating carbon monoxide & carbon oxide. The iron oxide is decreased to iron. The lance is retracted & the furnace is tapped by tilting it. The opening in the vessel is so provided that the slag still floats on the top of the molten metal as seen in Figure (c). The slag is then removed by tilting the furnace in the opposite direction.
The BOF process is capable of refining 250 tons of steel in 35 to 50 minutes. Most of the BOF steels, that are of better quality then open-hearth furnace steels and have low impurity levels, are processes into plates, sheets, and several structural shapes, such like I-beams & channels.Steel might also be melted in induction furnaces from which the air has been eliminated, similar to the one illustrated in Figure. The vacuum melting generates high quality steels because the process eliminates gaseous impurities from the molten metal.