Capping:
Capping of pre-mRNA occurs instantly after synthesis and involves the addition of 7-methylguanosine (m7G) to the 5' end in the figure. To get this, the terminal 5' phosphate is first erased through a phosphatase. The Guanosyl transferase then catalyzes a reaction whereby the resulting diphosphate 5' end attacks the phosphorus atom of a GTP molecule to add a G residue in an unusual 5' 5' triphosphate link that shown in the figure. The G residue is then methylated through a methyl transferase adding a methyl set to the N-7 position of the guanine ring by using S-adenosyl methionine as methyl donor. That structure with just the m7G in position is called a cap 0 structure.
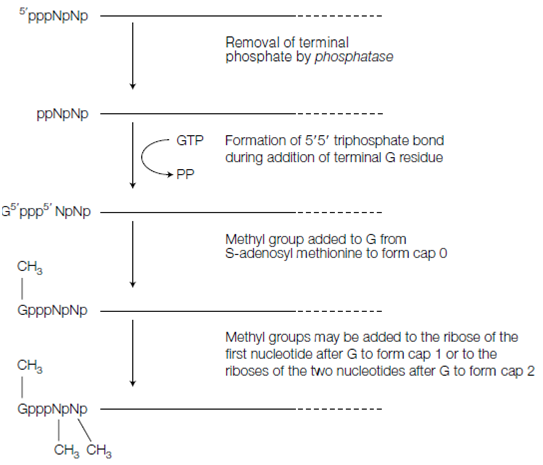
Figure: Steps involved in the formation of the 5' cap.
The ribose of the adjacent nucleotide or nucleotide 2 in the RNA chain or the riboses of both nucleotides 2 and 3 should also be methylated to provide cap 1 or cap 2 structures respectively. In these cases, the methyl sets are added to the 2' -OH groups of the ribose sugars shown in the figure.
The cap protects the 5' end of the main transcript against attack through ribonucleases which have specificity for 3' 5' phosphodiester bonds and so cannot hydrolyze the 5' 5' bond in the cap structure. Additionally, the cap plays a role in the initiation step of protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Only the RNA transcripts from eukaryotic protein-coding genes become capped; prokaryotic mRNA and eukaryotic tRNAs and rRNA are uncapped.