Process Planning for Parts
Once the decision has been taken for manufacture a part, the manufacturing processes will be decided according to the requirement of the materials from which the required material is formed. The materials selection decision shall be taken by the design engineer while designing the product itself.
There are four different processes are identified to manufacturing a part as illustrated in Figure 1.
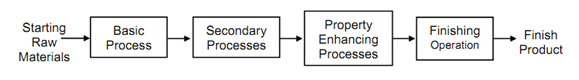
Figure 1 : Manufacturing Processes
The basic processes include metal casting, forging & sheet metal rolling. In the basic process, it establishes the initial geometry of the part.
Secondary Processes
The secondary process transforms the basic snap in to ultimate geometry of the part. There is a correlation among secondary processes and basic process to minimise the overall processes.
Example 1
For a specific Part
- Basic Process: Sand casting, Forging.
- Secondary Process : Machining.
Example 2
For Strips and Coils of a Sheet Metal
- Basic Process: Rolling.
- Secondary Process: Blanking, Punching and Bending.
In development of some parts there is no need of secondary process, which is based on the materials to be manufactured.
Example 3
Plastic Part Manufacturing
Basic Process: Injection moulding.
There is no need of secondary process, because finished product shall be produced in this basic process with required dimensional quality.
After these processes the third procedure is properyy enhancing process. In this process most of the materials properties have been altered. Most significant property enhancing process is heat treatment process.
Fourth and final procedure is finishing operation in this process sequence. Usually the most finishing operations are assembly or painting or coating of materials.
Process planning engineer's duty is to find out the most suitable processes and the order in which they must be manufactured. So that the overall cost must be minimised and the designed quality requirements must be fulfilled.