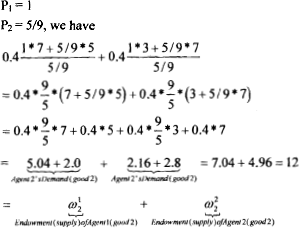Normalisation of Prices:
See that we have one equation in two unknowns, the prices. However, since we have a pure exchange economy without money, only relative prices matter, i.e., only the price ratio is important. That means, we can "normalise" on of the prices to 1 :Remark This result also comes from the homogeneity of degree 0 of the demand functions. Remember; by definition of homogeneity of degree 0 in prices we have: 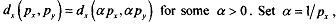
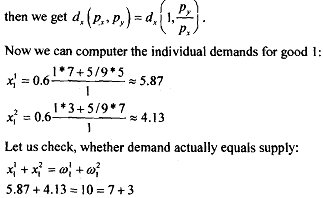
Second Market:
We solve for the other market, i.e., the market for. good 2. By Walras law, if one market clears the second also clears (if the total number of market is 2); thus using the prices computed above, we get the equilibrium demands for the market of good 2. Thus, from