Approach to Process FMECA
The failure modes recognized by the FMECA process are assessed by their probability of occurrence. To set up qualitative measures of occurrence, severity, & detection, criteria must be established that subjectively relate to the total effect on the process. Examples are given in the following Tables to serve as guide in setting up the measures. The product of the measures of occurrence, severity and detection is known as the Risk Priority Number (RPN). Tables (a) and (b) are for instance only. The numbers or criteria assigned to any specified ranking system are at the discretion of the user.
Table (a) : Severity Probabilities
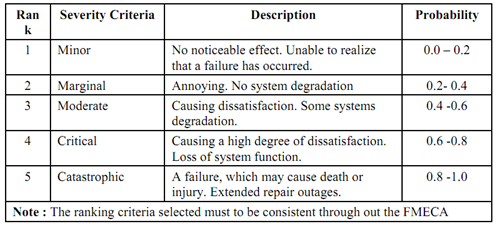
Table (b) : Occurrence Probabilities
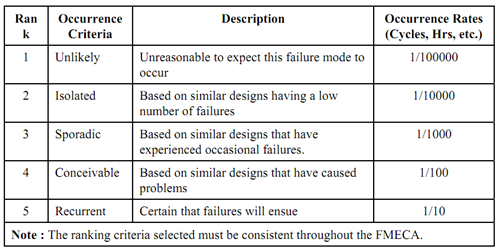
Table (c) : Detection Probabilities
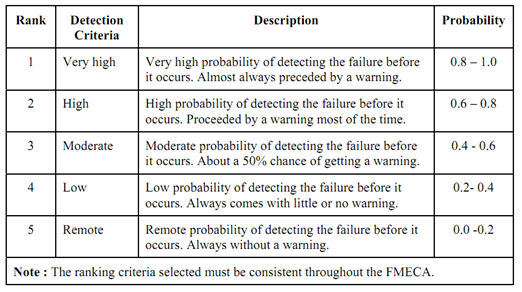
Table (d): Values Represent the Analyst's Judgment
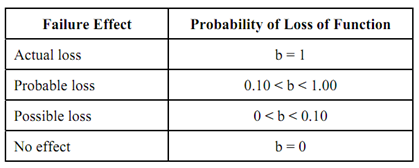
The failure mode and criticality number (Cm) is the portion of the criticality number for the item because of a particular failure mode. This criticality number replaces the RPN number utilized in the previous section. The Cm for failure mode is resolute by the expression.
Cm = b a lp t
Where b = conditional probability of loss of function,
a = failure mode ratio,
lp = part failure rate, and
t = duration or operating time.
The failure mode ratio, a, is the probability that the part or item shall fail, if all of potential failure modes of a particular part or item are listed, the total of all the probabilities for that part or item shall be equal to one. Individual failure mode multipliers might be derived from failure rate source data or from test & operational data. If failure mode data are not available, the value must represent the analyst's judgment depend on an analysis of the item's functions.
Part failure rates, lp, are derived from suitable reliability prediction methods by using Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) data or possibly other data attained from handbooks or reference material. Manufacturers frequently supply failure data; though, it is important that the item shall be similar to the environment the manufacturer utilized when attaining the failure data.
The operating time, 't', is generally expressed in hours or the number of operating cycles of the item being analysed. The 'a' and 'b' values are frequently subjective, therefore making the supposed quantitative method somewhat qualitative. All things considered, it is generally understood that the FMECA process is a qualitative method of analysis.