Process Capability
It is defined as the ratio of specification spread & process spread that means 6 times the standard deviation.
∴ C p = USL - LSL /6 σ
Where USL & LSL are the upper & lower specification limits, (USL - LSL) is the allowable specification spread. If the process might be sufficiently represented by a normal distribution, then the denominator is the process spread and is taken to be 6σ.
Cp = 1
Recommend that the specification spread equals the process spread. This means the process is just capable of meeting the specifications. In normal distribution tables, just a small proportion (0.0027) of products shall fall outside the specification limits supposing the process is centred b/w the specification limits.
If Cp >> 1,
then the specification spread is much larger than the process spread & we say that the process is potentially capable of meeting the specification.
If Cp << 1,
then the specification spread is much less than the process spread & we say that the process is not capable of meeting the specification.
While the process mean is not centred or the specification is one-sided, then a more informative index is the Cpk index. Cpk is computed as the smaller of the following two values.
- The USL minus the process avg. divided by 3σ.
- The process avg. minus the LSL, divided by 3σ.
Mathematically,
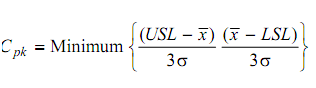
provided that
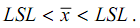
This index compares the minimum deviation of the process mean x from either specification to half the process spread.
Cpk as a Measure of Quality
Quality losses may be calculated using:
A. The conventional method.
B. The quality loss function method.