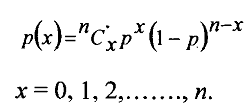Binomial Distribution
The binomial distribution is an example of a discrete probability distribution. It signifies two possible outcomes of an experiment, the occurrence of an event or the non-occurrence of the event. A probability experiment can be termed as a Bernoulli experiment, if it satisfies the following conditions.
1) The experiment consists of a sequence of n repeated trials.
2) Each trial results in an outcome that may be classified either as a success or a failure.
3) The probability of a success, denoted by p, is known and remains the same. in each trial. Consequently, the probability of a failure, denoted by q = (1 -p) is also known and remains the same in each trial.
4) The trials are independent.
The probability of x successes in n trials is given by