Setting Pricing Policy
Pricing policy setting begin with setting the pricing objective that may be: Profit Oriented (concerned by increase in profit), Sales Oriented (mainly concerned with increase in sales) and Status Quo Oriented. While costs set the lower limit of prices, the demand and market set the upper limit. Consumer and industrial buyers balance the price of a product or service both against the benefits of owning it.
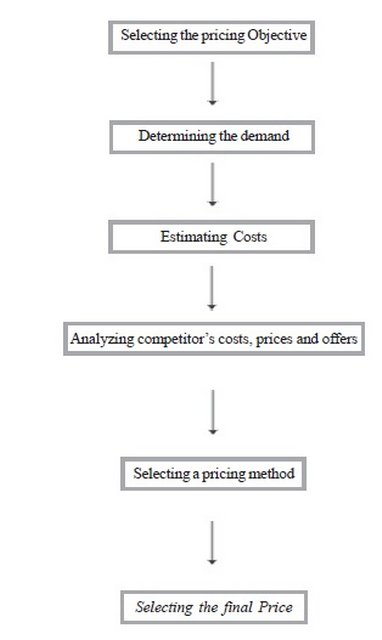
Therefore, before setting prices, the marketer has to understand the relationship between price and demand for its product. In this section, we described how the price-demand relationship varies for different markets and how buyer perceptions of price influence the pricing decision. Costs set the floor for the price that the company may charge for its product. The company desires to charge a price that both covers all its costs for distributing, producing and selling the product and delivers a fair rate of return for its risk and effort. A company's costs can be an important element in its pricing strategy. Companies with lower costs may set lower prices that result in greater profits and sales. Company's pricing decisions are also influence by competitors' and prices and costs and possible competitor reactions to the company's own pricing moves therefore whereas setting the prices theses facts should also kept in mind. Last step is setting the ending price using different methods.