C-C bond formation:
Aromatic carboxylic acids can be acquired through the oxidation of alkyl benzenes. It does not issue how large the alkyl group is, because they are all oxidized to a benzoic acid structure.
There are two ways by which alkyl halides can be transformed to a carboxylic acid and in both cases, the carbon chain is extended through one carbon. One way includes substituting the halogen along with a cyanide ion, then hydrolyzing the cyanide group. This acts best with primary alkyl halides. Another method involves the creation of a Grignard reagent that is then treated with carbon dioxide.
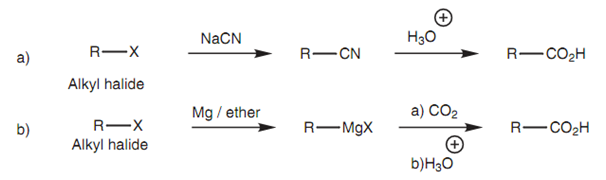
Figure: Synthetic routes from an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid.
The mechanism for Grignard reaction is identical to the nucleophilic addition of a Grignard reagent to an aldehyde or ketone as shown in figure.
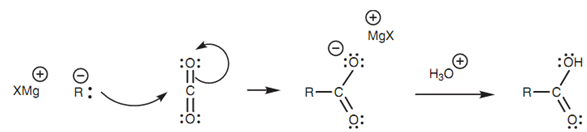
Figure: Mechanism for the Grignard reaction with carbon dioxide.
A variety of carboxylic acids can be prepared through alkylating diethyl malonate, after that hydrolyzing and decarboxylating the product as displayed below.
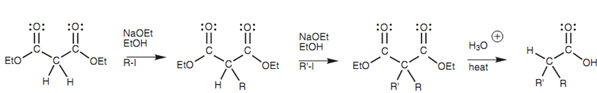
Figure: Synthesis of carboxylic acids from diethyl malonate.