Parallel resonance:
Refer to the circuit diagram of Figure given below. It is a parallel RLC circuit. In this case, the resistance R is taken as a conductance G, with G = 1/R. Then circuit can be known as GLC circuit.the
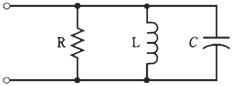
Figure-- A parallel RLC circuit.
At some specific frequency fo, inductive susceptance BL will exactly cancel the capacitive susceptance BC; which menas, BL=-BC. It is inevitable for some frequency fo, as long as circuit contains finite, nonzero inductance, nonzero capacitance.
At frequency fo, the susceptances cancel out each other out, leaving zero suscep tance. The admittance through circuit is then nearly equal to the conductance, G, of resistor. If the circuit has no resistor, but a coil and capacitor only, it is called as parallel LC circuit, and admittance at resonance will be very low. The circuit will offer great opposition to ac at fo. Engineers think more often in the terms of impedance than in terms of admittance; low admittance translates into th high impedance. This condition is termed as parallel resonance.