Composite Shafts - Series Connection:
If two or more shafts of different types of materials, lengths & diameters are connected in such a way that each carries the same torque, after that a composite shaft linked in series is produced. Figure shows such a shaft in which shafts AB, BC and CD are connected in series and their characteristics such as diameter, length and modulus of rigidity are explained in figure. The composite may also be regarded as stepped shaft.
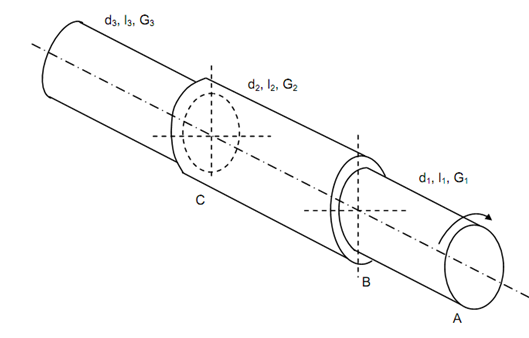
Figure
As each of AB, BC and CD is subjected to same torque T, then from Eq.
T = J1 G1 θ1/ l1 = J 2 G2 θ2/ l2 = J3 G3 θ3/ l3
where, θ1 = θBA , θ2 = θCB , θ3 = θDC
where θBA means angle of twist of section A with respect to B.
Therefore,
θDA = θ1 + θ2 + θ3
= T l1 / J1 G1 + T l2 / J 2 G2 + T l3 / J3 G3
Or θDA /T = l1 /J1G1 + l2 /J2G2+ l3/J3G3
We have described the ratio T as torsional stiffness which is understood as torque per unit twist. Also, Torsional stiffness is referred to as spring constant of the shaft and denoted by k. It is obvious that shaft and for others T / θDA is the spring constant of the composite shaft and for others
K1 = T/ θ1= J1 G1/ l1, k1 = T/ θ2 = J 2 G2/ l2 , k = T/ θ3 = J3 G3/ l3
Therefore, Eq. (i) can be written as
1 / k = 1 / k1 + 1/ k2 + 1/k3
Here, k is referring to spring constant or torsional stiffness of the composite shaft.