Fuses and breakers:
A fuse is a piece of soft wire which melts, breaking a circuit if current exceeds a certain level. Fuses are placed in the series with transformer primary. Any short circuit, component failure, or overload which might cause catastrophic damage will burn fuse out. Fuses are easy to replace, although it is aggravating if the fuse blows and you do not have replacements.
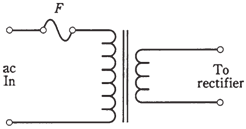
Figure-- A fuse, F, in series with the ac input protects the transformer and diode, in case of overload.
If the fuse blows, it should be replaced with another of same rating. If the replacement fuse is rated too low in current, it will probably blow out right away, or soon after it has been installed. If replacement fuse is rated too high in current, it may not protect the equipment. Fuses are available in 2 types: quick-break and slow-blow. You can usually recognize a slow blow fuse by spring inside. A quick break fuse has a wire or foil strip. While replacing the fuse, use right kind of wire. Quick break fuses in slow blow situations might burn out unnecessarily; slow blow units in quick break environments will not provide proper protection.
Circuit breakers do same thing as fuses, except that the breaker can be reset by turning off power supply, waiting a moment, and then pressing the button or flipping a switch. Some breakers automatically reset when the equipment has been shut off for a certain length of time. If a fuse or breaker keeps blowing out often, or if it blows immediately after you have replaced or reset it, then something is wrong with supply or with equipment connected to it.