Load Balancing
Load Balancing is the procedure of achieving and maintaining equal load on each phase of a distribution transformer. The loadings on primary and secondary side of a DTR are shown in Figure.
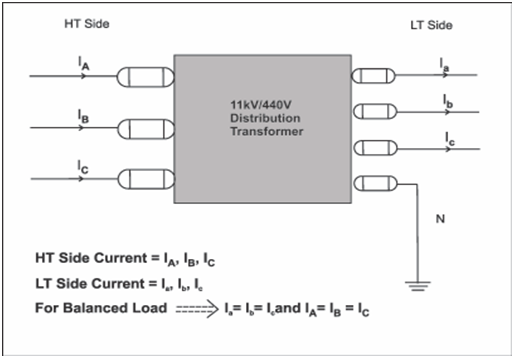
Figure: Balancing of Load in a DTR
If load on every phase of the distribution transformer is not equal, it is known as unbalanced loading of transformer. Practically speaking, balanced load cannot be managed on the transformer because of the inherently varying nature of load. Each transformer supplies power to resistive loads (bulbs, heaters, etc.) and inductive loads (motors, etc.). These loads could be either single phase, distributed separately on the three phases, or three-phase in nature. If the distribution transformer is supplying power to only three phase loads, then achieving and maintaining balanced load on transformer could be a simpler task. But in practice, this happens very rarely, since each installation possesses either three phase or single phase or both the loads, that keep changing at various points of time.
Apart from natural unbalancing, unbalanced load might also result from load shedding of one phase in every of the LT feeders emanating from a distribution substation. Even by the system might have been balanced initially, it is hard to have same loaded outgoing feeders and achieve equal load shedding in the three phases. In some cases, because of constraints on availability of proper switching facility on each feeder, it is hard to shed equal load from each phase. Therefore, it is really a difficult task for a distribution utility to maintain balanced load on the distribution transformer. However, it is important for several purposes.