Direct Potentiometry:
Potentiometric methods of analysis may be grouped into direct reading method or direct potentiometry and potentiometric titrations. In this section we are taking up direct potentiometry in detail. Within following section, the potentiometric titrations will be discussed.
The direct potentiometry is the method which makes use of the single measured electrode potential to determine the activity of the ion of interest (or concentration of the ion in case of dilute solution). This technique is hugely used for the determination of pH of the solution (by using Hydrogen electrode) or determinations of other ions using variant ion-selective electrodes.
In all the electroanalytical methods, there are two electrodes are needed, the potential of one of the electrode be known, constant and is fully independent of the composition of the solution. This electrode is called as Reference electrode.
The second electrode whose potential is dependent on the concentration of the ion to be determined is known as indicator electrode. For direct potentiometric measurement, the potential of the cell can be expressed in terms of the potential developed by the indicator electrode and the reference electrode:
Ecell = (Eind - Eref ) + Ej ... (2.16)
where Ej is a junction potential.
Consider the indicator electrode whose potential vary with cation activities or concentration, we could write Nernst Equation same to Eq. 2.3 derived previously for half cell reaction expressed through Eq. 2.1:
Eind = Eºind + (0.0591/n)log a Mn+ ...(2.17)
Substitution of Eq. 2.17 into Eq. 2.16 yields:
Ecell = (Eºind + (0.0591/n)log aMn+) -Eref +Ej ...(2.18)
On rearrangement
log aMn+ = n(Ecell - k)/ 0.0591 ...(2.19)
or pM =log aMn+ = n(Ecell - k)/ 0.0591 ...(2.20)
For anion An- Eq. 2.20 will have reversed sign
pA = -log aAn+= n(Ecell - k)/ 0.0591 ... (2.21)
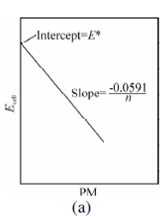
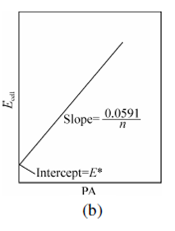
Figure: (a) A plot of Eq. 2.22 for a metal ion electrode; (b) A plot of Eq. 2.23 for an anion electrode
where pM and pA are the negative logarithm of the metal ion activity aMn+ and an anion aAn+, respectively. These terms are more general forms of the familiar term pH. K is summation of several constants, involving standard electrode potential of metal ion or anion and potential of reference electrode, junction potential, and asymmetrical potential if membrane electrode is involved.