Glycogen:
A glycogen molecule consists entirely of glucose units, many of that are connected in long chains through α1-4 bonds. Moreover, every 10 units or so, the chain is branched through the Formation of an α1-6 glycosidic bond. Each straight- chain segment of glycogen establish an open helix conformation that increases its accessibility to the enzymes of glycogen metabolism. Every chain terminates in a nonreducing end, which is, an end with a free 4′ OH group. Because the enzyme which degrades glycogen (glycogen phosphorylase) catalyzes the sequential erased of glycosyl units from the nonreducing end of a glycogen chain the numerous branches, each with a nonreducing end, greatly raise the accessibility of the polysaccharide to degradation. This permits rapid mobilization of stored glycogen in times of required. The α1-6 branches themselves are erased through a debranching enzyme.
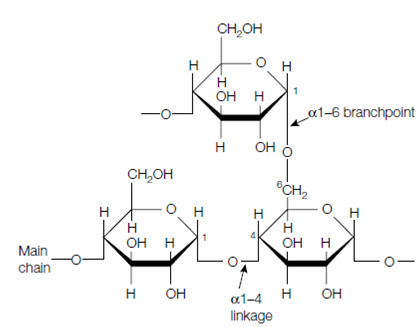
Figure: The 1-4 linkages in the straight chain and 1-6 branchpoint linkages in glycogen.