Electrolysis:
In During electrolysis, chemical reactions occur under the influence of an electromotive force at electrodes immersed in solutions. A reaction occurring at the electrodes i.e. electrode reactions are characterized by the transfer of electrons between the electrode and the substances in the solution. Since of this the equality of positive and negative ions are unbalanced at the electrode but is counter acted by oppositely directed movement of positive and negative ions through the solution to produce the flow of current through the solution.
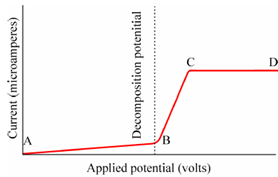
Figure: A Typical Polarogram
This is the current which is actually measured by the movement of electrons in the external circuit connecting the two electrodes. Thus, the current is the output of the electrode reaction. An electrode at that reduction occurs is the "cathode" and electrode at which oxidation occurs is the "anode". The curve acquire by plotting e.m.f. applied to a cell against the resulting current is the current-voltage curve.
When the applied potential is equal to the decomposition potential (B) of the electroactive substance (e.g. Zn2+) at the cathode the current starts increasing because ofthe following cathodic reaction.
Zn2+ + 2e- + Hg ↔ Zn (Hg)
The resulting zinc will form amalgam along with mercury on the surface of the mercury electrode. Since the potential of the dropping mercury electrode (micro electrode) is made more negative, there is a additional increase in current in accordance along with Ohm's law and the concentration of Zn2+ is decreased at the electrode surface until at point C the concentration at electrode surface is negligibly small in comparison along with that in the bulk of the solution. Here from C to D the current remains constant this is determined by the rate of diffusion of Zn2+ ions from the bulk of the solution to the electrode surface. The number of Zn2+ ions diffusing from the bulk of the solution to the electrode surface is equal to the number that is deposited when the steady state is reached or the rate of diffusion is equal to the rate of reduction.