Manufacturing Process For Reinforced Plastic Parts
Two procedures namely open mould and close mould are commonly utilized for manufacture of reinforced parts. Hand layup procedure consists in applying a thin coat of gel mat on the gel coated mould or on the open surface of mould, laying fibreglass cloth and brushing the matrix resin on the fibres. The liquid resin might also be poured or sprayed. The catalysts and accelerators are added to the resin before pouring. The brushed surface is rolled with rollers for eliminating entrapped air and spreading resin evenly. The woven fibre or cloth is added as selective sites in the mould to enhance thickness of the part as per design requirement. Tanks, boat hulls and panels are built by this procedure. Hand lay up process is illustrated in Figure.
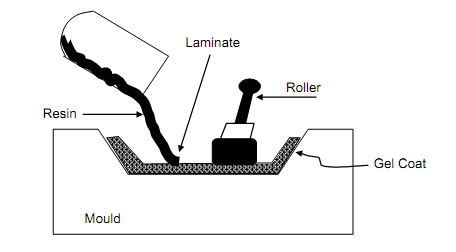
Figure: Hand Lay Up Process
In a slight variation, to suit the requirement of bigger size parts the fibre rovings and resin are simultaneously fed. The fibre rovings are fed through a chopper whereas a spray gun sprays the catalysed resin. The rollers are utilized in the same way as in case of hand lay ups. The process is known as spray-up illustrated in Figure.
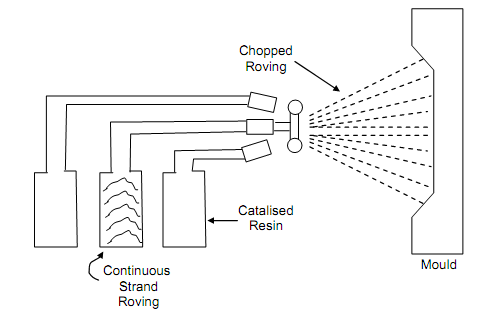
Figure: Spray Up Process
In vacuum bag-autoclave process long carbon fibres are primary impregnated in resin and laid out on flat table. After epoxy gets cured partially the prepregs are placed on shaped tool in distinct directions and thickness. The tool covered along prepregs and desired shape and thickness is placed in vacuum bag that is placed in autoclave. It causes final curing of the epoxy. The part is stripped from tool & finished to needed dimensions. Vacuum bag procedure results in parts of high strength, light weight, and stiffness. Critical parts like aeroplane wings, cargo bay doors and parts of rudder of space shuttle are built by this process. The parts incur high cost and therefore are not utilized widely.
Hollow cylinders are built by filament-winding procedure wherein fibres are built to pass through resin bath and wound on a mandrel. A wound resin-fibre composite is cured either at room temperature or elevated temperature on mandrel itself. After the curing is done, the cylinder is eliminated from mandrel. The procedure resulting in high strength due to stretched fibres is utilized for making pressure vesssels, piping for fuels and chemicals and casing for rocket motor.
In closed mould procedure, the glass fibres mixed with resin might be injected in a mould. In yet another procedure the chopped fibres are continuously fed on the top of polyethylene film. On the top of fibres the resin paste is laid which is constantly covered with another polyethylene film generating a sandwiched sheet of composite. The procedure is automated and continuous. Further these sheets are stored in maturation rooms for one to four days. These sheets are cut to size, placed in a heated metal mould and pressed under hydraulic pressure to attain shape of the mould and uniform thickness. The procedure called sheet-moulding compound procedure is capable of generating high production volume of uniform products with good surface finish. Auto body parts are being generated by this process.
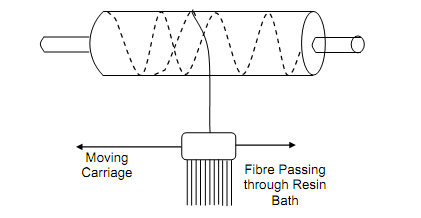
Figure: Filament Winding
Structure sections of long length are generated by putting the fibres through resin bath and heated dies of particular shapes. Unidirectional fibres with high volume fraction and pretensioning procedure are capable of producing high strength. The procedure is known as continuous pultrusion. The schematic pultrusion process is illustrated in Figure.
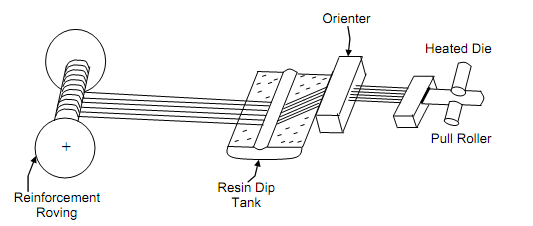
Figure: Pultrusion