Inductively Coupled Plasma:
The inductively coupled plasma (ICP) is plasma induced by radiofrequency. The energy transfer is mediated by an induction in that produces a magnetic field which is helps in establishing and sustaining the plasma. The energy of a high frequency generator is transferred to a gas, commonly argon, flowing at atmospheric pressure. A typical inductively coupled plasma source is called a torch. The most common ICP torch in use today has evolved over decades of development. It consists of a quartz tube whose upper part is surrounded by a radiofrequency work coil. The torch assembly is designed to deliver gases so that stable argon plasma is formed at the open end through which the sample aerosol can be injected. Let us learn about the different components of the ICP torch and their functions.
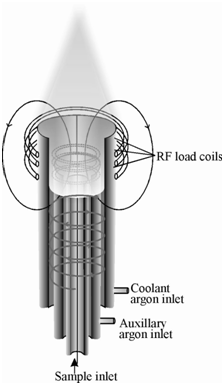
Figure: A schematic section diagram of an ICP torch