Viroids and satellites
Viroids are small, naked circular infectious ssRNA molecules of just a few hundred nucleotides that form the smallest known pathogens of plants. Unlike viruses, viroids have no capsid and appear to encode no mRNA or proteins. Viroids are spread by plant
Figure: Focal assay of tobacco mosaic virus on the leaf of a plant.
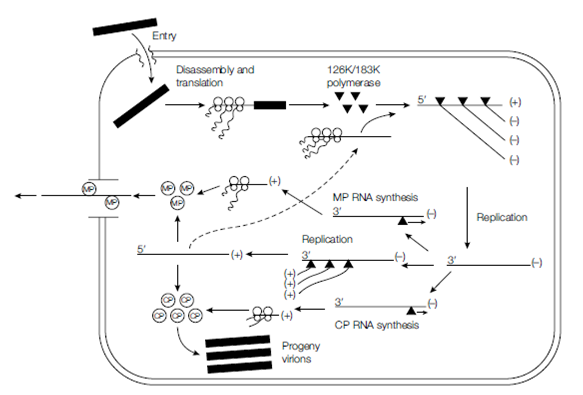
Figure: Diagram of stages of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) infection. All the events shown are presumed to occur in the cytoplasm of infected cells. MP, movement protein; CP, coat protein.
propagation (e.g. cuttings and tubers), through seeds, and by manual mishandling with contaminated implements. Approximately 25 viroids have been identified to date and they can cause serious plant diseases. The first to be examined in detail was potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd), which is responsible for significant annual loss to the potato industry. The RNA is a covalently closed circle and ranges in size from 246 to 357 nucleotides in length. The RNA has a complex secondary and tertiary structure, which gives it a rod-like shape and resistance to nucleases. The RNA does not have a characteristic open reading frame and so does not act as mRNA. How this piece of RNA causes disease is largely unknown, but it is thought that it may interfere with either the action or selectivity of the host cell RNA polymerase II enzyme, or with RNA splicing.
Satellites are dependent pathogens that require host cell or helper virus proteins for full replication. They are of two types: satellite viruses encode their own capsid protein while satellite nucleic acids are enclosed in the capsid of a helper virus infecting the same host cell. The hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a satellite nucleic acid comprising a circular RNA molecule of 1700 nucleotides, and is the smallest known pathogen of humans. HDV only replicates in cells infected with HBV and as a result its transmission and treatment are linked to that of its helper virus, HBV. The HDV genome encodes two proteins, known as delta antigens, and their presence appears to contribute to the replication of both satel- lite and helper, often leading to severe clinical outcome.