Superposition Theorem
The theory of superposition gives us ability to decrease a complexes problem to many easier problems - each of containing just a single independent source - states that
"In a linear circuit having multiple sources, the voltage or current at any point in the circuit can be calculated by the algebraic sum of the specific contributions of each source acting alone." Any left behind sources of current will make zero from replacing it by open circuit & any voltage sources will make zero from replacing it by short circuit at the time of determining the contributions because of independent sources
Example: Compute the value of Vo by applying principle of superposition.
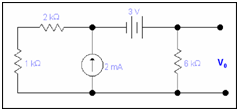
Solution: By applying principle of superposition, we will consider effect of the sources one by one.
When only voltage source is active
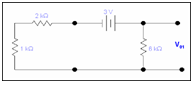
By applying voltage division rule we will get
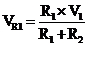
V01 = V6k = (6 x3)/3+6
V01 =2 V
When only current source is active
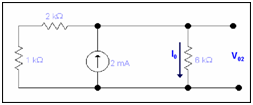
Assume the current flow through 6k resistor is I0
Now by applying current division rule we will get
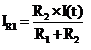
I0 = (3 x 2)/9 = 2/3 mA
V02 = I0 x 6k
=2/3m x 6k = 4volts
Therefore V0 will be
V0 = V02 + V01
= 4volts +2volts = 6Volts