Linearity Principle
In this method we suppose the unknown quantity & analyze the circuit in reverse manner. Still we attain the source which is generating all voltages or currents and compute its value.
Now by comparing this value along with the main value of the source we determine the precise unknown quantity of any circuit.
Example: Determine Vo by using linearity principle.
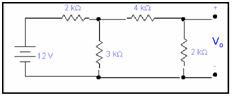
Sol:
We have to calculate Vo via linearity principle. Let us suppose that Vo is equal to 1 Volt.
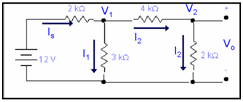
From assumption Vo=1V
So, V2=1V
And so I2=1/2k=0.5mA
And, V4k= (0.5m)(4k)=2Volts
Now we can say V1=V4k+V2= 2+1= 3V
After that, I1=3/3k=1ma
and, Is=I2+I1=0.5m+1m=1.5mA
V2k=Is(2k)=2k(1.5m)=3Volts
Vs=V2k+V1=3+3=6Volts
While Vo is equal to 1, source voltage is 6V, but original source voltage is 12 V, thus output voltage is 2 Volts.