Solvent effect on the stabilization:
One time the ammonium ion is formed, it is solvated via water molecules - a stabilizing factor that involves hydrogen bonding among the oxygen atom of water and any N-H group present in the ammonium ion. The much more hydro- gen bonds which are possible, the greater the stabilization. The outcome of it is solvation and solvent stabilization is stronger for alkylaminium ions made from primary amines than for those formed from tertiary amines. The solvent effect tends to be more significant than the inductive effect as far as tertiary amines are concerned and thus tertiary amines are usually weaker bases than primary or secondary amines.
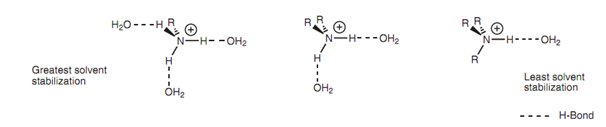
Figure: Solvent effect on the stabilization of alkylammonium ions.