Resonance interaction between nitrogen’s lone pair and the aromatic ring:
Aromatic amines (arylamines) are weaker bases as compare to the alkylamines as the orbital containing nitrogen's lone pair of electrons overlaps with the π system of the aromatic ring. In terms of resonance, the lone pair of electrons can be employed to make a double bond to the aromatic ring, resultant in the chance of three zwitterionic resonance structures. (A zwitterion is a molecule consisting of a positive and a negative charge.) As nitrogen's lone pair of electrons is involved in this interaction, it is less available to make a bond to a proton and thus the amine is less basic.
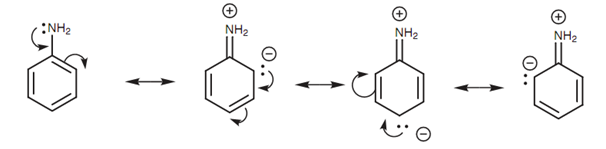
Figure: Resonance interaction between nitrogen's lone pair and the aromatic ring.
The nature of aromatic substituent as well influences the Basicity of aromatic amines. Substituents that deactivate aromatic rings (that is NO2, Cl, or CN) lower electron density in the ring that means that the ring will encompass an electron-withdrawing effect on the neighboring ammonium ion. The meaning of this is that the charge will be destabilized and the amine will be a weaker base. Substituents that activate the aromatic ring improve electron density in the ring which means that the ring will encompass an electron-donating effect on the neighboring charge. This has a stabilizing effect and thus the amine will be a stronger base. The relative position of aromatic substituents can be significant if resonance is possible among the aromatic ring and the substituent. In such types of cases, the substituent will have a greater influence if it is at the ortho or para position. For instance, para-nitroaniline is a weaker base than as compared to the meta-nitroaniline. This is since one of the possible resonance structures for the para isomer is highly disfavored because it places a positive charge immediately next to the ammonium ion. Hence, the number of possible resonance structures for the para isomer is limited to three, compared to 4 for the meta isomer. Here the meaning is that the para isomer experiences less stabilization and thus the amine will be less basic.