Pathway:
Under general atmospheric conditions, rubisco adds CO2 to ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate. Moreover, when the CO2 concentration is low, it can add O2 as an alternative. This generates phosphoglycolate and 3-phosphoglycerate. A phosphoglycolate can be salvaged and used for biosynthetic reactions but the pathway for achieving this releases CO2 and NH4 and wastes metabolic energy. Since the net result of this procedure is to consume O2 and release CO2, it is known as photorespiration. This is a main problem for plants in hot climates. The plants close the gas replace pores in their leaves (stomata) to conserve water but this leads to a drop in the CO2 concentration within the leaf, favoring photorespiration. Additionally, as temperature increase, the oxygenase activity of rubisco (using O2) raise more rapidly than the carboxylase activity (using CO2), again favoring photorespiration. To prevent these problems, some plants adapted to live in hot climates, such as corn and sugar cane which have evolved a mechanism to maximize the carboxylase activity of rubisco. In this plant carbon fixation using the Calvin cycle takes place only in bundle-sheath cells which are protected from the air through mesophyll cells. Since the bundle-sheath cells are not showing to air and the O2 concentration is low. The CO2 is transported from the air through the mesophyll cells to the bundle-sheath cells through combining with three-carbon molecules (C3) to produce four-carbon molecules (C4). These enter the bundle-sheath cells where they are broken down to C3 compounds and releasing CO2. The C3 molecules revisit to the mesophyll cell to accept more CO2. These cycles ensures a high CO2 concentration for the carboxylase activity of rubisco action in the bundle- sheath cells. Because it relies on CO2 transport through four-carbon molecules, it is known as the C4 pathway and plants which use this mechanism are known as C4 plants. All other plants are known as C3 plants since they trap CO2 straightly as the three- carbon compound 3-phosphoglycerate.
Details of the C4 pathway are shown in Figure. The steps included are as follows:
- phosphoenolpyruvate (C3) accepts CO2 to form oxaloacetate (C4); a reaction catalyzed through phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in the mesophyll cell
- Oxaloacetate is transformed to malate (C4) by NADP+ linked malate dehydrogenase
- malate enters the bundle-sheath cell and releases CO2, creating pyruvate (C3); catalyzed through NADP+ -linked malate enzyme
- Pyruvate proceeds to the mesophyll cell and is used to regenerate phosphoenolpyruvate. This reaction, catalyzed through pyruvate-Pi dikinase, is unusual in which it needs ATP and Pi and breaks a high-energy bond to produce AMP and pyrophosphate.
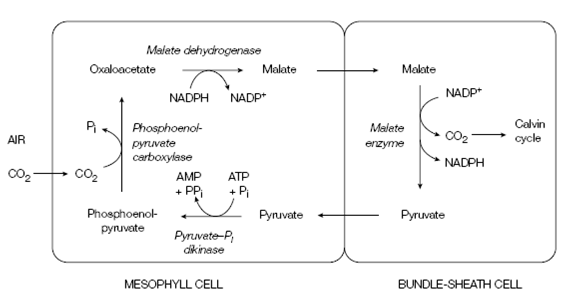
Figure: The C4 pathway.
The pyrophosphate from the pyruvate-Pi dikinase is rapidly degraded so that, whole, the total price the plant pays for operation of this CO2 pump is the hydrolysis of two high-energy phosphate bonds for every molecule of CO 2 transported:
CO2 (in air) +ATP → CO2 (bundle-sheath cell) +AMP +2 Pi