Dark reactions:
The dark reactions (also called the carbon-fixation reactions) use the NADPH and ATP produced through the light reactions to convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrate. The last products are starch and sucrose.
The key carbon fixation reaction is catalyzed through a huge enzyme known as ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (frequently abbreviated to rubisco) which is situated in the stroma. The reaction condenses a carbon die oxide molecule with ribulose 1, 5- bisphosphate (a five-carbon molecule) to produce a transient six-carbon intermediate which rapidly hydrolyzes to two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate shown in the figure:
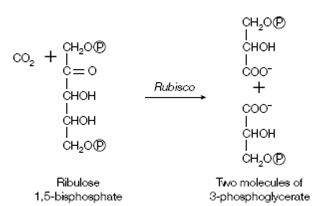
Figure: The rubisco reaction.
Rubisco is a very slow enzyme, fixing only three molecules of its substrate every second and thus a huge amount of this enzyme is required through each plant. Classically, rubisco accounts for 50 percent or so of the total protein in a chloroplast. Certainly, it is possibly the most abundant protein on earth!
The rubisco reaction forms element of a cycle of reactions that is known as the Calvin cycle, which leads to the reproduction of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (ready to fix other CO2) and the net production of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate for the synthesis of sucrose and starch. There are three molecules of CO2 that must be fixed to generate one molecule of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (a three-carbon molecule). The whole reaction for this is:
3CO2+6NADPH+9ATP→glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate+6NADP++9ADP+8Pi
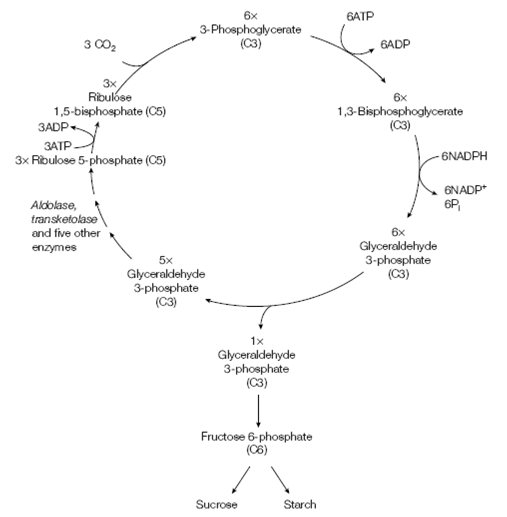
Figure: The Calvin cycle.
The several reactions are shown in Figure. Following the creation of six molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate, six NADPHs and six ATPs are used to produce six molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Simply one of these molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is then used to create fructose 6-phosphate and, ultimately, starch. The another five molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate are transformed in a series of steps (including transketolase, aldolase and five other enzymes) to three molecules of ribulose 5-phosphate that are then phosphorylated (using three molecules of ATP) to create three molecules of ribulose 1,5- bisphosphate, prepared for another turn of the cycle. Therefore one complete turn of the cycle, trapping the three molecules of CO2 as one molecule of glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate, requires 6+3= 9 ATPs and 6 NADPHs.