Cyclic photo- phosphorylation:
When the NADPH/NADP+ ratio are high and little NADP+ is available to accept electrons and in other words electron transport pathway is used which included only PSI and a few electron carriers. Here the high-energy electron is passed through ferredoxin to the cytochrome bf complex in its place of to NADP+. It then flows to plastocyanin and back to the P700 of PSI. The resulting proton gradient produced from the H+ pump and cytochrome bf complex, then drives ATP synthesis. In during this cyclic photophosphorylation, ATP is created but no NADPH is made. In addition, since PSII is not included, no O2 is produced.
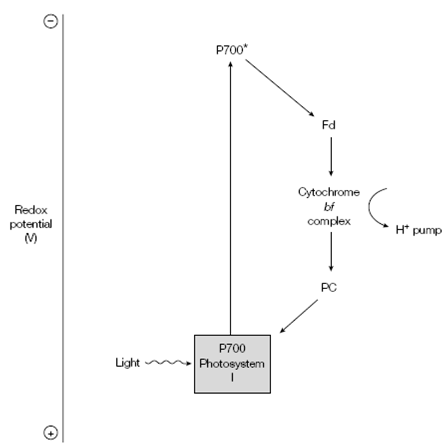
Figure: Cyclic photophosphorylation in green plants. Note that the arrows in this diagram represent the sequence of events during photosynthesis, as described in the text, and are not metabolic interconversions.
In short, when electron transport is operating in noncyclic mode, through PSII and PSI, the products are ATP and NADPH. In cyclic electron transport, on the other hand ATP is the sole product.