Main reactions of the pathway:
The center reactions of the pathway can be summarized as follows:

The pathway has three stages:
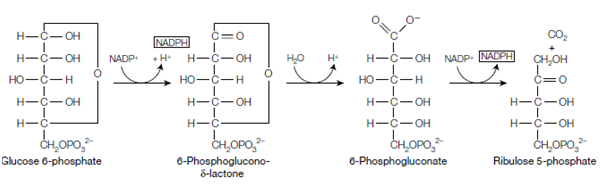
Stage 1 - Oxidative reactions which convert glucose 6-phosphate into ribulose 5-phosphate generating two NADPH molecules
Glucose 6-phosphate is oxidized through glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase to 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone (producing NADPH) and this is then hydrolyzed through lactonase to 6-phosphogluconate. 6-phosphogluconate is then converted through 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase to ribulose 5-phosphate. This is an oxidative decarboxylation for instance the 6-phosphogluconate is oxidized and a carbon is removed as CO2. These reactions are shown as follows:
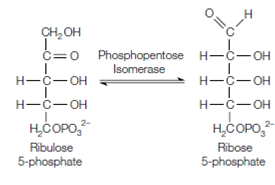
Stage 2 - Isomerization of ribulose 5-phosphate to ribose 5-phosphate
the ribulose 5-phosphate is now converted to ribose 5-phosphate through isomerization, a reaction catalyzed through phosphopentose isomerase:
Stage 3 - Linkage of the pentose phosphate pathway to glycolysis via transke- tolase and transaldolase
If at any time only a little ribose 5-phosphate is needed for nucleic acid synthesis and other synthetic reactions it will tend to build up and is then converted to fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate through the enzymes transketolase and transaldolase. These two products are midway of glycolysis. Thus, these reactions provide a link among the pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis. The outline reactions are shown follows.
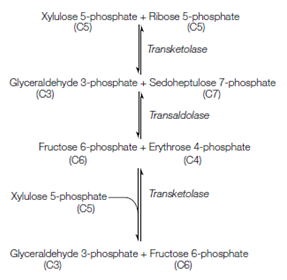
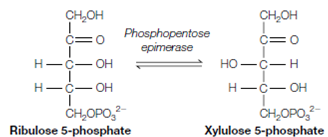
Details of these reactions, displaying the structures of the molecules included, are given in Figure. These reactions need xylulose 5-phosphate as well as ribose-5- phosphate. The Xylulose 5-phosphate is an epimer of ribulose 5- phosphate and is establish through phosphopentose epimerase:
Whole the reactions in this stage can be summarized as:
