Multi view Projections:
A multi view projection displays a single face of a three-dimensional object. General choices for viewing an object in two dimensions involved the front, side, and top or planar view. The view plane normal in the world coordinate system axis is placed along one of the major axis for each of the multi view projections. In the top view, the view plane normal is parallel with the positive y-axis in a right-handed system. Figure illustrates a top or planar view of the three-dimensional building shown in Figure (a). To project the top view of the 3-D object, the y-coordinates are discarded & the x- and z-coordinates for each of point are mapped to the view plane. By repositioning the view plane normal to the positive z-axis and choosing the x- and y-coordinates for each of point, a front view is projected to the view plane (Figure (b)). Likewise, a side view (Figure (c)) results when the view plane normal is directed along the positive x-axis and the y- and z-coordinates of a three-dimensional object are projected to the view plane. These projections are frequently used in engineering and architectural drawings (Hearn and Baker, 1996). When they do not illustrate the three-dimensional aspects of an object, multi view projections are useful as the angles and dimensions of the object are maintained. Figure shows all the six views, which may be obtained in particular case of orthographic projections.
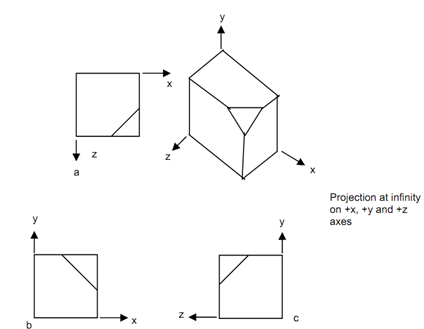
Figure: Orthographic Projection on to (a) y = 0; (b) z = 0; and (c) x = 0